The zygote divides to form two- celled proembryo. The larger cell positioned closer to the micropyle is termed the basal or suspensor initial cell, while the smaller cell closer to the chalaza is referred to as the terminal or embryonal initial cell. The suspensor cell divides in a single plane, transversely, leading to the formation of a filamentous suspensor consisting of 6 to 10 cells.
The initial cell of the suspensor closest to the micropylar end enlarges and functions as a haustorium. The lowest cell of the suspensor is termed the hypophysis. The suspensor helps in pushing the embryo in the endosperm. The embryonal initial undergoes three successive mitotic divisions to form octant. The planes of divisions are at right angles to each other.
The lower group of four cells within the octant gives rise to the hypocotyl and radicle, while the upper group of four cells forms the plumule along with one or two cotyledons. Through further division, the hypophysis contributes to the development of the radicle and root cap.
Subsequently, the cells in the upper tier of octant divide in several planes so as to become heart shaped which then forms two lateral cotyledons and a terminal plumule. Further enlargement of hypocotyl and cotyledons result in a curvature of embryo and it appears horse-shoe shaped. The embryo development is similar in both dicots and monocots up to the octant stage. The difference appears later.
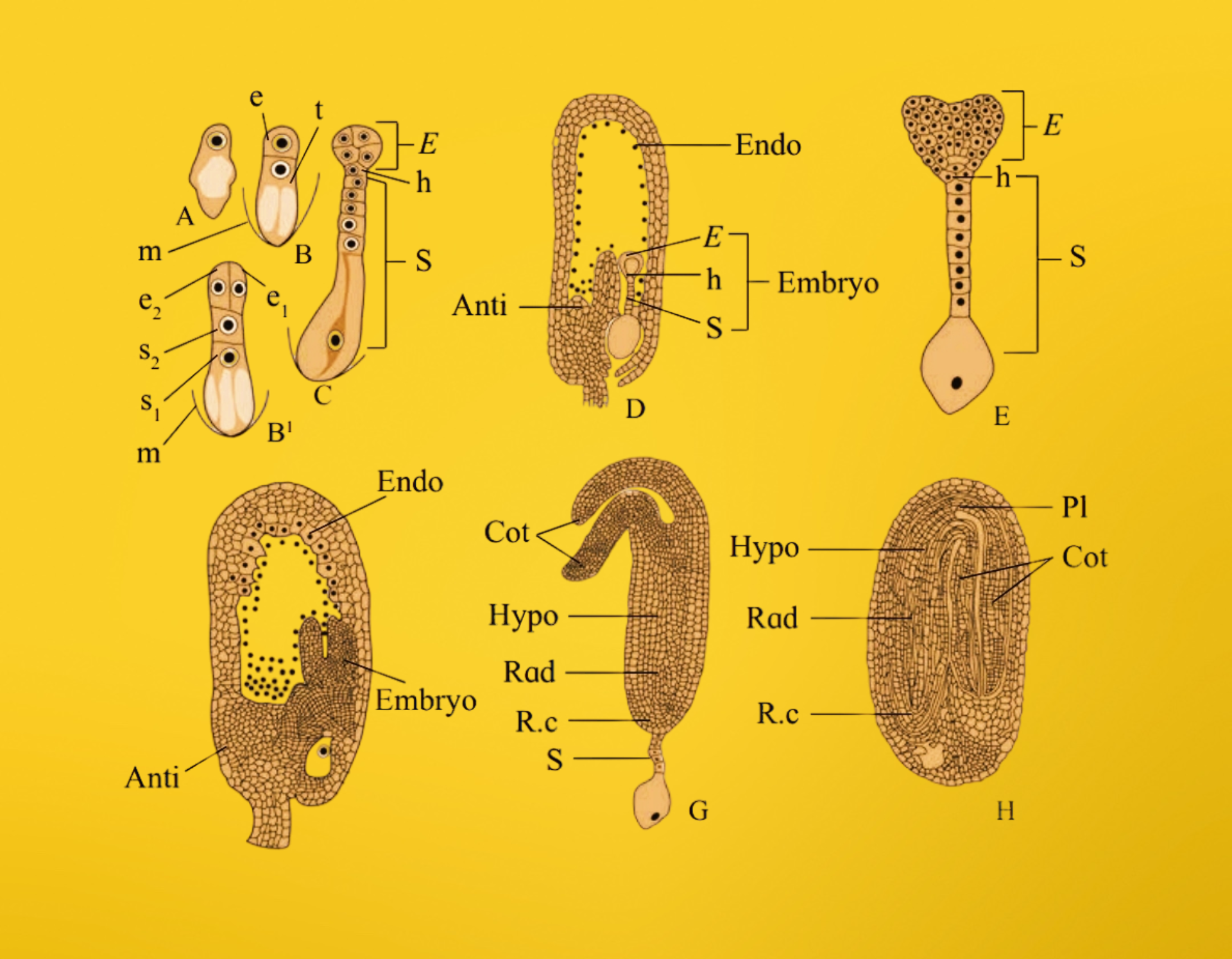
- A. Oospore
- B. Two celled
proembryo. e=embryonal initial; t=suspensor initial; m=Embryo sac membrane. B1 =4-celled I-shaped
proembryo; e1, e2 are from embryonal initial; s1, s2 are from suspensor initial. - C. Further development of embryo. S=Suspensor, h=Hypophysis; E=Embryonal mass
- D. L. S. of ovule Endo=Endosperm in free nuclear stage. Anti=Antipodal tissue. Embryo= Developing embryo
- E. Embryo showing further development of embryonic octants and hypophysis.
- F. L. S. of ovule. Endosperm becoming cellular.
- G. Embryo Cot=Cotyledons; Hypo=Hypocotyl; Rad=Radicle; R.c=Root-cap
- H. Mature seed. Pl=Plumule. Endosperm has been consumed almost completely.