A dihybrid cross occurs when two pairs of alleles are involved, resulting in a phenotypic ratio of 9:3:3:1 in the F2 generation, known as the dihybrid ratio.
For example,
- When we mate a true-breeding pea plant with round and yellow seeds with another true-breeding pea plant having wrinkled and green seeds, the offspring in the F1 generation will have round and yellow seeds.
- Upon self-pollination of F1 plants, the F2 generation exhibits a ratio of 9:3:3:1, with 9 plants having yellow round seeds, 3 plants having yellow wrinkled seeds, 3 plants having green round seeds, and 1 plant having green wrinkled seeds.
- Parents (P1) : RRYY × rryy
Gametes of P1 RY and ry
F1 generation : RrYy(Yellow round)
On selfing F1 : RrYy × RrYy
Gametes of F1 : RY, Ry, rY, ry
P2 generation: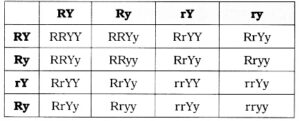
In terms of phenotype, the ratio is 9 Round Yellow : 3 Round Green : 3 Wrinkled Yellow : 1 Wrinkled Green, represented as 9:3:3:1.
In genotypic terms, the ratio is 1:2:1:2:4:2:1:2:1.