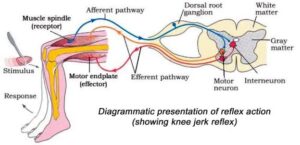
1. Receptor organs, such as the skin, eyes, tongue, nose, and ears, specialize in converting stimuli into impulses.
2. Sensory neurons transport these impulses from the receptors to the central nervous system, with their cell bodies in the dorsal root ganglion.
3. Motor neurons, located in the ventral horn of the spinal cord, convey motor impulses to effector organs like muscles and glands, prompting a response.